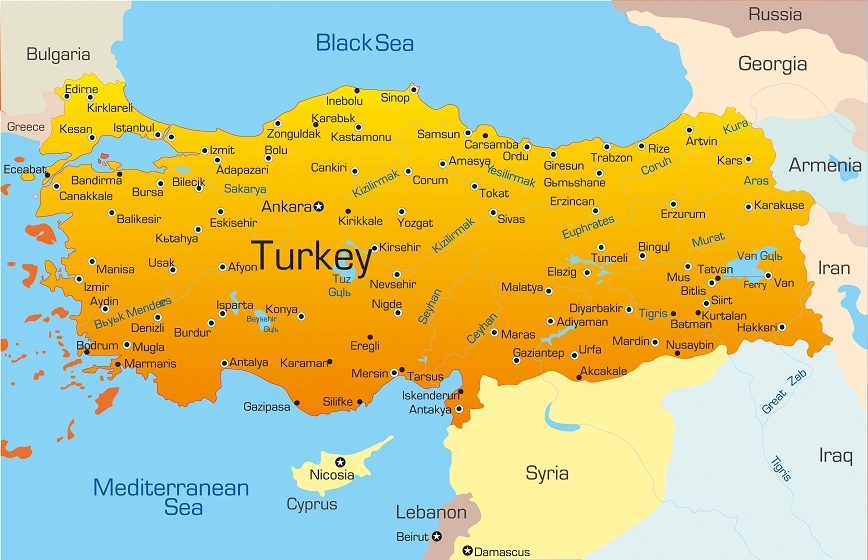
Turkey is a large country spanning Europe into Asia. It has amazing geography that boasts sea, mountains, rivers and volcanoes.
Turkey is situated between Europe and Asia. Its geography is very diverse and everything from snow topped mountains to sandy beaches can be found in this country. Turkey lies between 35-42° north latitude and 25-44° east longitude. The total land area of Turkey is 779,452 km2. Turkey has land borders with seven countries: Syria, Iraq, Iran, Georgia, Armenia, Greece and Bulgaria. Turkey has approximately 8400 kilometres of coastline on the Mediterranean and the Aegean Sea. The highest mountain in Turkey is Mount Ararat which is 5165 metres tall. In order to examine the geography of Turkey close we will look at four main regions.
Geography of Eastern Turkey
The climate in the east of Turkey is generally cooler than other parts of the country with an average temperature of just 9.5°C. The geography is mainly mountainous although the local people do produce wheat crops and also graze sheep. In the South East of Turkey close to the borders of Syria and Iraq the weather is slightly warmer with especially hot summers where the temperature can reach as high as 48°C. This part of the country is also drier with comparatively less rainfall than other areas although the rivers Tigris and Euphrates both originate in this part of Turkey.
Geography of Black Sea Areas of Turkey
Turkey has a coastline on the Black Sea which extends across its northern borders from the extreme west to the east of the country. The geography towards the Eastern part of Turkey there are mountain ranges which reach right down to the coast and meet the sea. Temperatures in this part of the country fluctuate between 43°C near the coastal areas during summer, right down to -34°C in some of the more high altitude areas. This part of Turkey sees the most rain with average annual rainfall at 781 mm. The northern part of Turkey is known for its hazelnuts and cherries which are grown in abundance, however perhaps more unusually there are tea plantations on the slopes of some of the mountainous areas.
Geography of Central Anatolia
The capital city of Turkey is situated in central Anatolia and stands nearly 1 km above sea level. The geography of this part of Turkey is formed of high land plateaus although there are some mountain ranges and even volcanoes. Similar to the Eastern part of Turkey wheat is grown and sheep are grazed. Temperatures can drop to as low as -34°C degrees during winter however this rises to above 40°C in the summer.
Geography of Western Turkey
The Western part of Turkey is known as Marmara and contains Turkey’s largest city Istanbul, as well as a coastline on the Aegean Sea. The geography in this part of turkey consists mostly of rolling hills which are suitable both for the grazing of animals and farming. The soil here is particularly rich and grapes, apricots, olives, figs, tobacco peaches all thrive here. Temperatures here are moderate with fluctuations between approximately 30-40°C, and average humidity at just under 70%.