Learning Spanish reflexive verbs? Read on to find out the meaning of Spanish reflexive word…
Spanish reflexive verbs basically refer to actions which you perform on yourself. When you’re trying to understand Spanish reflexive verbs you should know that they are categorized under pronouns.
Most people find it very complicated, but one should remember that every time you speak about an action that is being performed on yourself you are exemplifying the reflexive nature of this action by utilizing a reflexive verb.
Spanish Reflexive Verbs Explained
Spanish reflexive verbs indicate that the subject being referred to in the sentence has performed an act on itself. This basically means that in a Spanish reflexive sentence the object and the subject are the same.
For example if we speak about different examples to illustrate the use of the Spanish reflexive verbs than you can say the following sentences:
Trina woke up. She put on her shoes. Longoria became sick. Mina asked herself a question. The boy brushed his hair.
Now in the last example a question may arise that the object is hair and why is that a Spanish reflexive verb? However, Spanish language does not incorporate parts of the body by preceding them with personal pronouns.
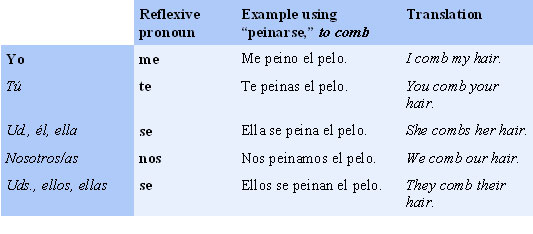
To further illustrate this statement you can say that in Spanish language one would never refer to teeth as my teeth rather they would be spoken about as the teeth with the Spanish reflexive verb preceding it. In English one would say I comb my hair whereas in Spanish one would say Me peino el pelo which translates into I comb the hair.
Spanish Reflexive Verbs Preceded by Reflexive Pronouns
All of the Spanish reflexive verbs are preceded by Spanish reflexive pronouns. A simple list of these is as follows: Yo is preceded by the reflexive pronoun me in the example using ‘peinarse’ which means to comb – I comb my hair.
Identifying Reflexive Verbs
To figure out when a Spanish verb is reflexive and when it is not you will have to check the ending. For a Spanish reflexive verb it would end in –se present in the infinitive form. The common reflexive verbs can be explained by statements like: to be happy which is translated as alegrase, to get angry – enojarse, to wash yourself -lavarse and to brush yourself cepillarse. Similarly if the word does not have the –se attached to it then it is not a reflexive verb.
Emotions in the Spanish Reflexive Verb
If you’re using an emotional phrase like I am angry, I’m happy or I am sad you will be using the Spanish reflexive verb in most cases. When you say how you feel and you are expressing your current emotional state, then you will be using estar with descriptive adjectives as mentioned above.
However, if you need to show a passage of time in which your emotional state was changing you will use the Spanish reflexive verb. Example for this context can be ‘It made me sad, I got angry quickly, it always makes me happy to hear you sing’.
Is a very simple nuance in terms of the Spanish language and it is fairly easy to pick up in a natural manner when you start utilizing Spanish reflexive verbs in speech. At this point you will be able to identify the difference between utilizing a Spanish reflexive verb and combining an estar with descriptive adjectives which will both allow you to express emotions.